Combining meta-analysis with data visualization to identify success factors in new models for health care payment and service delivery
As part of the 2010 Affordable Care Act, Congress authorized the Center for Medicare and Medicaid Innovation to test innovative health care payment and service delivery models with the potential to lower Medicare, Medicaid, and Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP) expenditures while maintaining or improving the quality of beneficiaries’ care.
In July 2012, more than 100 providers, payers, local government, public-private partnerships, and multi-payer collaboratives received awards ranging from approximately $1–30 million over a three-year period to implement these innovative models. Known as the Health Care Innovation Awards, this initiative was open-ended rather than prescriptive, meaning the awardees could focus on innovations in care coordination, care management, home care, telemedicine, or any other aspect of service delivery or payment—with specific, shared goals of improving outcomes and reducing costs.
In the years since, these innovative programs have been subject to evaluation, producing vast amounts of information about what works in particular circumstances.
To move the discussion from “Does it work?” to “Would it work in my setting?”—a question that must be answered to support adoption of a successful model by other providers or agencies—requires fully characterizing the intervention, analyzing and synthesizing immense amounts of sometimes contradictory data, and understanding the methods used to produce it.
Using Meta-analysis to Understand Results across Evaluation Studies
On behalf of CMMI our experts developed a new combination of approaches to analyze the Health Care Innovation Awards to make the lessons available more useful for policy makers and other health care stakeholders.
By looking across multiple studies and placing their results on a common scale, meta-analysis allows us to understand evaluation results in a different way. Our approach draws on additional sources of information—about the interventions, implementation, outcome measurement, and evaluation design—to understand the differences between study findings and examine relationships across studies.
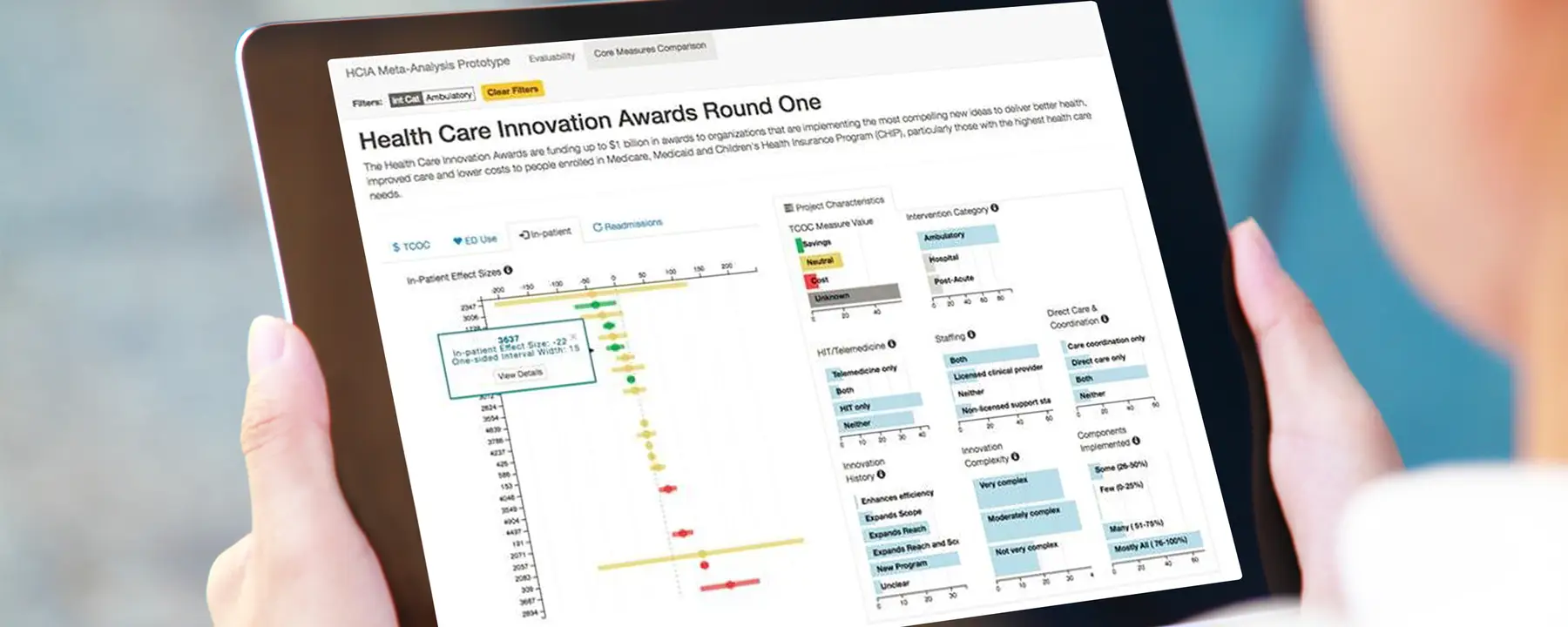
Informing Policy through Data Visualization
In addition to collecting and analyzing qualitative and quantitative data, we also developed a data dashboard to assist policy makers in understanding and using the wealth of information about HCIA interventions generated by our meta-evaluation. The dashboard is interactive, which allows decision makers to filter by key features of interest and understand the relationship of those features to programmatic effects. Without conducting extensive analyses, it is possible to examine characteristics of potentially promising models for future testing.
Identifying Models that Lower Health Care Costs and Improve Care
Using this approach, which relies on innovations in collecting, assembling, and displaying different sources of information, our meta-evaluation is able to identify health care payment and service delivery models that lower total costs of care while maintaining or improving the quality of beneficiaries’ care.
This offers a strategic aid to policy makers and to providers and agencies seeking to extend the benefits of successful health care innovations to reach more patients and realize the goals of health care reform.
- Center for Medicare and Medicaid Innovation